Configuration
Kubero UI
Customize the Kubero configuration
Allways edit the kuberoes CRD to make changes in your Kubero configuration. Changes on the configmap will be overwritten by the operator.
kubectl edit kuberoes kubero -n kubero
The config has three sections so far:
- kubero: configures the UI
- buildpacks: the selectable list of buildpacks
- podSizeList: the selectable list of pods
A full example can be found here https://github.com/kubero-dev/kubero/blob/main/config.yaml
kubero:
readonly: false
banner:
show: false
message: "Welcome to Kubero!"
bgcolor: "#8560A9"
fontcolor: "azure"
auth:
github:
# set your secrets in the secret resource
enabled: false
id: ""
callbackUrl: ""
org: ""
oauth2:
enabled: false
name: ""
id: ""
authUrl: ""
tokenUrl: ""
secret: ""
callbackUrl: ""
scope: "" # space seperated list of scopes
auditLogs:
enabled: false
storageClassName:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
size: 0.1Gi
limit: 1000
clusterissuer: letsencrypt-prod
templates:
enabled: true
catalogs:
- name: "Kubero"
description: "Kubero templates"
templateBasePath: "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubero-dev/kubero/main/services/"
index:
url: "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubero-dev/templates/main/index.json"
format: "json" # json or yaml # TODO has no effect yet. json is always used
- name: "Kubero Frameworks"
description: "Kubero frameworks"
templateBasePath: "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubero-dev/kubero/main/services/"
index:
url: "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubero-dev/templates/main/index-frameworks.json"
format: "json" # json or yaml # TODO has no effect yet. json is always used
buildpacks:
- name: NodeJS # displayed Name
language: JavaScript # Language detection match
fetch:
repository: ghcr.io/kubero-dev/fetch
tag: main
build:
repository: node # image to use
tag: latest # tag to use
command: "npm install" # command to run
run:
repository: node
tag: latest
command: "node index.js"
podSizeList:
- name: small
description: 'Small (CPU: 0.25, Memory: 0.5Gi)'
default: true
# resources are defined as usual in Kubernetes
# https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/manage-resources-containers/
resources:
requests:
memory: 0.5Gi
cpu: 250m
limits:
memory: 1Gi
cpu: 500m
CD/CD Buildpipeline
Building Docker images is a standard process in CI/CD pipelines. Kubero supports building images using these three methods: buildpacks.io, Nixpacks and Dockerfiles.
Once built, these images must be pushed to a container registry, which is configured in the kubero Custom
Resource Definition (CRD). The target registry must have a valid TLS certificate, Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN),
and basic authentication enabled for security. You can use a public (v2) registry like docker.io or ghcr.io,
or set up a local registry by enabling the create flag.
If you opt for a local registry, ensure that it is configured as an insecure registry on all nodes in the cluster. For details on configuring insecure registries, see the Docker CLI documentation.
This config requires Kubero Operator >= v0.0.137
spec:
registry:
enabled: true # creates registry credentials for a external or a local registry (required for build strategy apps)
create: true # spins up a local registry
#host: registry.kubero.svc.cluster.local # works for pushes, but not for pulls. DO NOT USE THIS :( since it requires to configure all nodes ot acceppt this "insecure" registry
#host: docker.io # requires a docker account. Might be the best choice when running on a non public domain
host: registry.mykubero.com # will make your images publicly avaialble with a basic auth protection
account:
# create account with:
# docker run --entrypoint htpasswd httpd:2 -Bbn [username] [password]
# http://aspirine.org/htpasswd_en.html (use bcrypt)
username: MyUser
password: MyPassword
hash: $2y$05$cXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
port: 443
storage: 1Gi
storageClassName:
Authentication
The Kubero UI has a built-in authentication to restrict access. All methods can be used simultaneously.
Local
This setup is suitable for individual users or very small teams (up to 8 credentials). Authentication credentials are stored in the environment variable KUBERO_USERS as a base64-encoded string.
Do not use this example credentials
1) create an encrypted password
PASSWORD=asdf &&
SALT=asdf &&
echo -n $PASSWORD | openssl dgst -sha256 -hmac $SALT
2) create a JSON file with the encrypted password. For example users.json
[
{
"id": 1,
"method": "local",
"username": "asdf",
"password": "8a8423ba78c8f3da60a602493663c1cdc248a89541b12980e292399c0f0cad21",
"insecure": false
"apitoken": "asdf",
},
{
"id": 2,
"method": "local",
"username": "qwer",
"password": "qwer",
"insecure": true,
"apitoken": "asdf",
}
]
3) encode the created file to base64
cat users.json | base64
4) put the env var in your secrets.yaml and apply it
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: kubero-secrets
type: Opaque
data:
...
...
stringData:
KUBERO_USERS: "WwogIHsKICAgICJpZCI6IDEsCiAgICAibWV0aG9kIjogImxvY2FsIiwKICAgICJ1c2VybmFtZSI6ICJhc2RmIiwKICAgICJwYXNzd29yZCI6ICI4YTg0MjNiYTc4YzhmM2RhNjBhNjAyNDkzNjYzYzFjZGMyNDhhODk1NDFiMTI5ODBlMjkyMzk5YzBmMGNhZDIxIiwKICAgICJpbnNlY3VyZSI6IGZhbHNlCiAgfSwKICB7CiAgICAiaWQiOiAyLAogICAgIm1ldGhvZCI6ICJsb2NhbCIsCiAgICAidXNlcm5hbWUiOiAicXdlciIsCiAgICAicGFzc3dvcmQiOiAicXdlciIsCiAgICAiaW5zZWN1cmUiOiB0cnVlCiAgfQpd"
...
...
kubectl apply -f secrets.yaml -n kubero
Github
If you already have a GitHub organization and want to grant access to its members, use this section.
go to organisation settings -> developer settings -> OAuth Apps and register an application
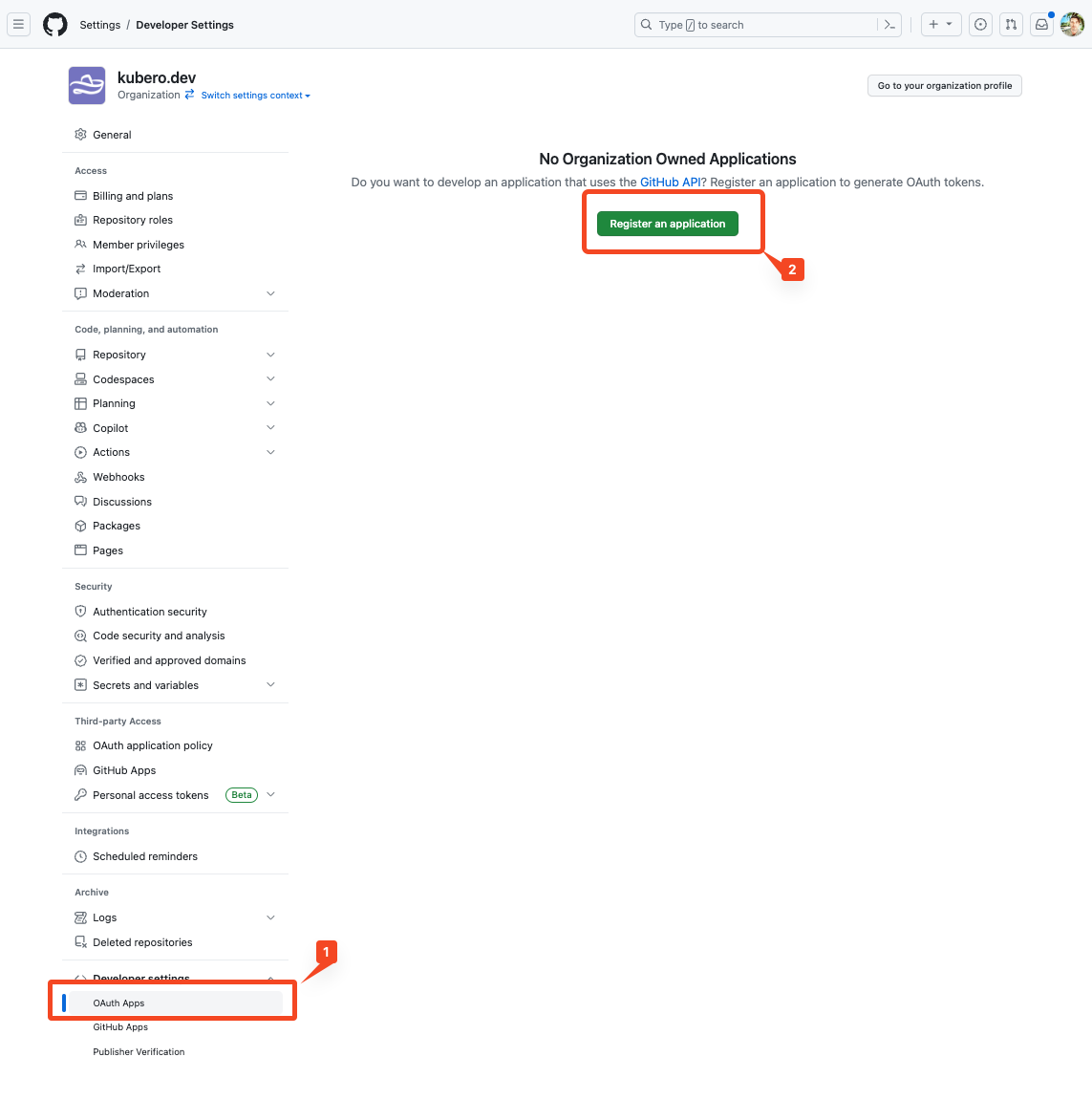
Choos a name and a homepage URL. Set the callback url to
https://<your-kubero-domain>/api/auth/github/callback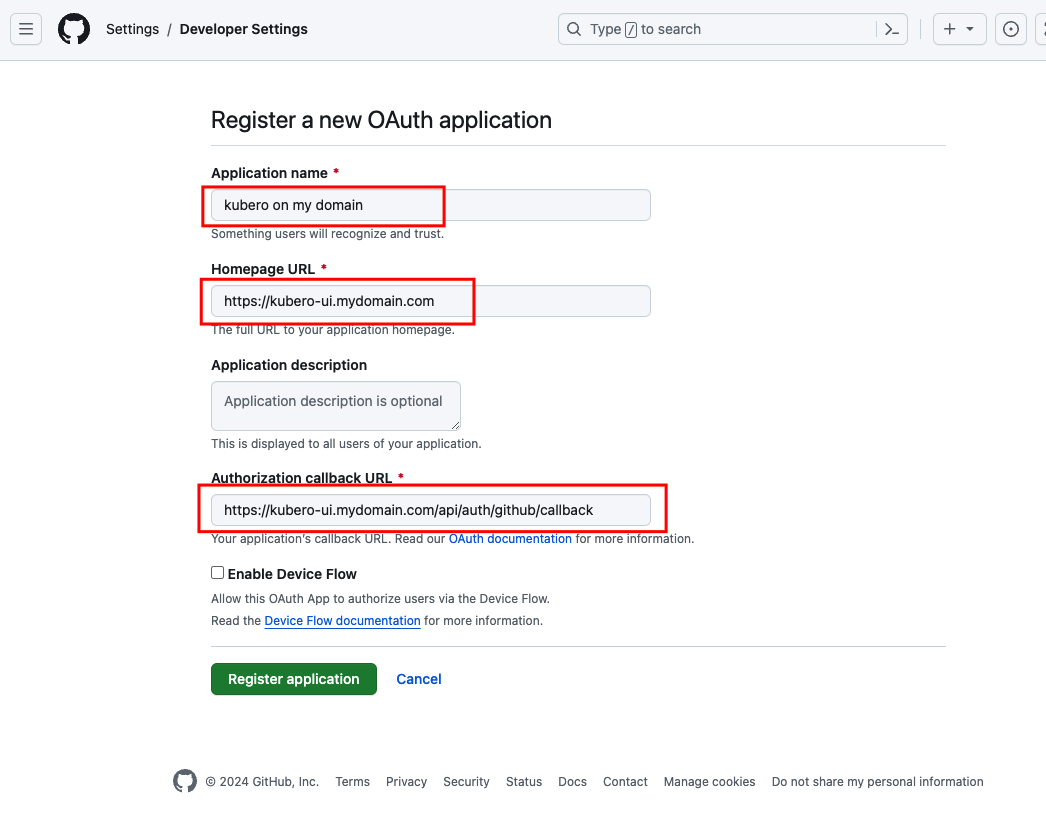
You will need the Client ID and the generated Client Secret
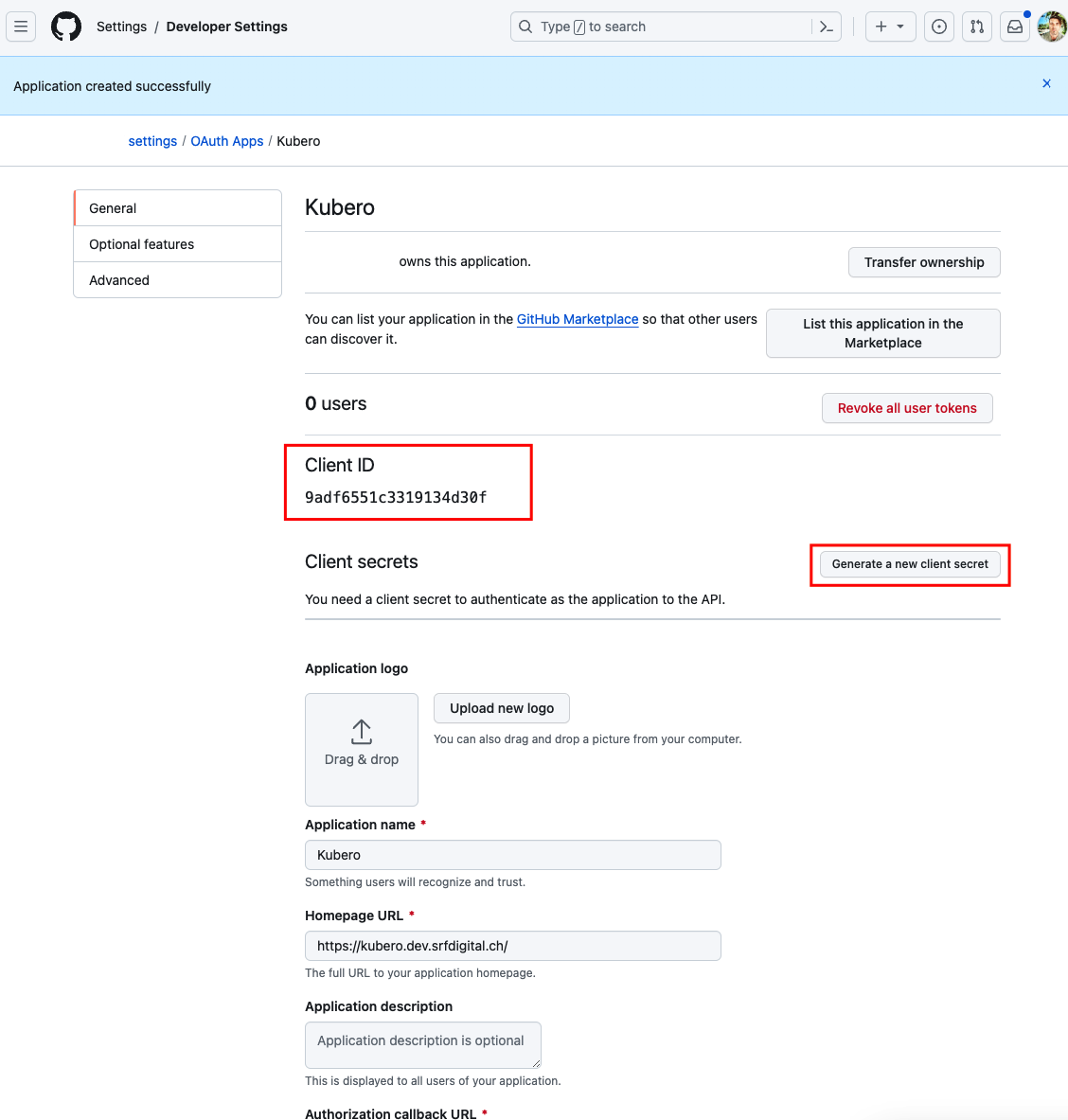
Configure the kubero UI
kubero:
auth:
github:
enabled: true
id: "<your client id>"
callbackUrl: "<your callback URL>"
org: "your-org" # this will limit access to this organisation
The Organisation needs to be public and visible in user profile. Private Organisations are not supported by Github since they are not accessible during login process.
- Add the "Client Secret" to secret
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: kubero-secrets
type: Opaque
stringData:
GITHUB_CLIENT_SECRET: <your client secret>
data:
...
...
Oauth2 (gitea, azure, keycloak, ...)
This should fit all other usecases.